Tuesday, December 22, 2015
Construindo um data warehouse com Pentaho e Docker
Thursday, December 17, 2015
Carlos Wizard Martins Lectures at Harvard
Marcadores:
Carlos Wizard Martins Lectures at Harvard
Friday, December 11, 2015
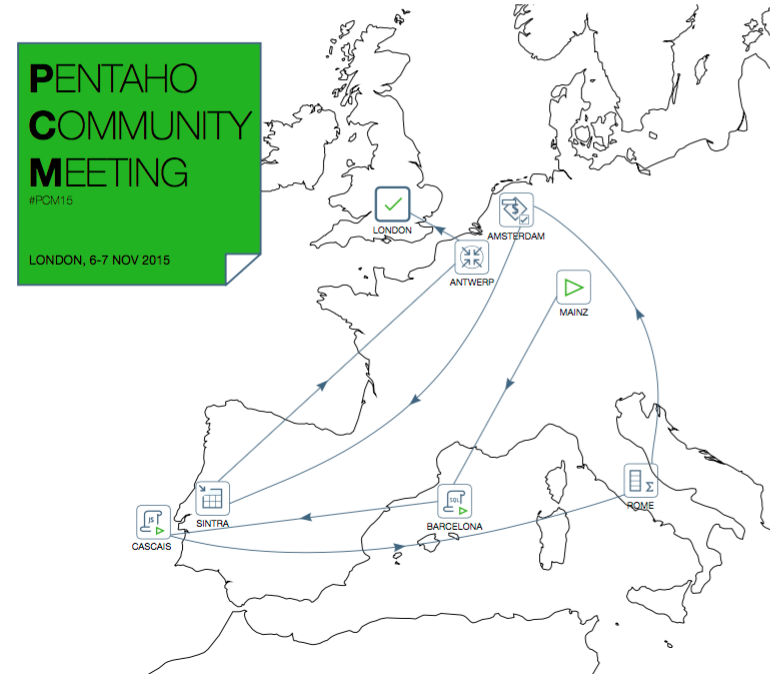
Pentaho Community Meeting 2015 - London, UK, Nov, 7, 2015
It is always amazing to participate in the PCM event.
Links:
http://diethardsteiner.github.io/pcm/2015/11/08/PCM15-Recap.html
https://github.com/PentahoCommunityMeetup2015/info
Links:
http://diethardsteiner.github.io/pcm/2015/11/08/PCM15-Recap.html
https://github.com/PentahoCommunityMeetup2015/info
Marcadores:
Pentaho Community Meeting 2015 - Recap
Thursday, December 10, 2015
Quer aprender muito sobre BI com Pentaho e ainda receber por isso?
Começar a trabalhar com BI é um grande desafio para muitos, afinal existem poucas empresas dispostas a te ajudar a aprender a dar os primeiros passos.
A IT4biz Global além de realizar projetos é referência na formação de profissionais de Business Intelligence Open Source, sendo pioneira no Brasil na utilização da Suite de BI Pentaho.
Se você deseja fazer um estágio em Business Intelligence em 2016 e aprender tudo sobre o assunto, envie um e-mail para rh@it4biz.com.br.
Estamos com vagas abertas para 2016 com início previsto para Janeiro ou Fevereiro de 2016.
Além de aprender muito, alguns estagiários foram incorporados pela IT4biz como consultores e muitos dos nossos ex-estagiários foram contratados por empresas como Oracle, Catho, Locaweb, etc.
Ficamos tristes por vê-los partir, mas felizes por saber que fizemos parte deste começo de carreira tão difícil.
A IT4biz Global possui atualmente projetos no Brasil, Espanha e Estados Unidos, e já realizou projetos em diversos outros lugares.
Temos escritórios em São Paulo, Brasil e Madrid, Espanha.
Somos super ativos na Comunidade Pentaho no Brasil e no Mundo, temos alguns projetos open source sendo utilizados por mais de 160 países e temos mais de 300 clientes espalhados pelo mundo.
Venha fazer parte!!!
Thursday, November 26, 2015
#Tips: How to delete backup from my mac
Hi Folks,
I had a lot of space in my Mac Book Pro dedicated to backups.
I want to share how to get this space back.
I had a lot of space in my Mac Book Pro dedicated to backups.
I want to share how to get this space back.
- Simply "turn off" Time Machine in its preference pane, under System Preferences.
- Turn it back on, or select "Back Up Now" in the title bar icon for TM, when you wish it to sync with your TC.
Alternatively, you can disable Local Snapshots as well, if you don't want to turn off Time Machine.
Enter this in Terminal:
sudo tmutil disablelocal
Source:
Marcadores:
#Tips: How to delete backup from my mac
Friday, November 20, 2015
#PCM2015 Facebook Pics - London, UK - Nov, 7, 2015
Pentaho Community Meetup - Nov, 7, 2015 - London - #PCM2015 Link:https://github.com/PentahoCommunityMeetup2015/info
Posted by Pentaho Brasil on Friday, November 20, 2015
Marcadores:
#PCM2015 Facebook Pics - London,
2015,
7,
UK - Nov
Let's Help / Vamos ayudar / Vamos ajudar Saiku Team #crowdfunding
Hi friends / Hola amigos/ Olá amigos,
EN: I still remember the day when Tom Barber presented PAT (Pentaho Analytics Tool) in Barcelona, Spain in 2009 at #PCM09.
ES: Yo aun me acuerdo el dia cuando Tom Barber presentó PAT (Pentaho Analysis Tool) en Barcelona, España en 2009 en #PCM09.
PT-BR: Eu ainda me lembro do dia quando Tom Barner apresentou PAT (Pentaho Analysis Tool) em Barcelona, Espanha em 2009 no #PCM09.
EN: Before PAT we were using jPivot and PAT was a very nice option to replace jPivot.
ES: Antes de PAT teniamos que utilizar el jPivot y PAT fue una muy buena opción para subsituir el jPivot.
PT-BR: Antes do PAT tinhamos que utilizar o jPivot e o PAT foi uma excelente opção para substituir o JPivot.
EN: Some years ago they changed the name to Saiku.
ES: Algunos años atras ellos cambiaron el nombre para Saiku.
PT-BR: Alguns anos atrás eles mudaram o nome para Saiku.
EN: The reason of this post is to help our friends from Saiku get money to improve this amazing Open Source Project.
ES: La razón de este post es para ayudar nuestros amigos de Saiku recebir diñero para mejorar este muy bueno proyecto de software libre.
PT-BT: A razão deste post é para ajudar nossos amigos do Saiku a conseguir dinheiro para melhorar este excelente projeto de software livre.
EN: Let's help them!!!
ES: Vamos a ayudarles!!!
PT-BR: Vamos ajudar!!!
Link to send them money: / Enlace para enviar diñero: / Link para enviar dinheiro:
http://kck.st/1MifvuZ
EN: I still remember the day when Tom Barber presented PAT (Pentaho Analytics Tool) in Barcelona, Spain in 2009 at #PCM09.
ES: Yo aun me acuerdo el dia cuando Tom Barber presentó PAT (Pentaho Analysis Tool) en Barcelona, España en 2009 en #PCM09.
PT-BR: Eu ainda me lembro do dia quando Tom Barner apresentou PAT (Pentaho Analysis Tool) em Barcelona, Espanha em 2009 no #PCM09.
EN: Before PAT we were using jPivot and PAT was a very nice option to replace jPivot.
ES: Antes de PAT teniamos que utilizar el jPivot y PAT fue una muy buena opción para subsituir el jPivot.
PT-BR: Antes do PAT tinhamos que utilizar o jPivot e o PAT foi uma excelente opção para substituir o JPivot.
EN: Some years ago they changed the name to Saiku.
ES: Algunos años atras ellos cambiaron el nombre para Saiku.
PT-BR: Alguns anos atrás eles mudaram o nome para Saiku.
EN: The reason of this post is to help our friends from Saiku get money to improve this amazing Open Source Project.
ES: La razón de este post es para ayudar nuestros amigos de Saiku recebir diñero para mejorar este muy bueno proyecto de software libre.
PT-BT: A razão deste post é para ajudar nossos amigos do Saiku a conseguir dinheiro para melhorar este excelente projeto de software livre.
EN: Let's help them!!!
ES: Vamos a ayudarles!!!
PT-BR: Vamos ajudar!!!
Link to send them money: / Enlace para enviar diñero: / Link para enviar dinheiro:
http://kck.st/1MifvuZ
Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Meet the Mormons Official Movie - Full HD
Marcadores:
Meet the Mormons Official Movie - Full HD
Monday, November 09, 2015
Thursday, November 05, 2015
#PCM15 - Pentaho Community Meeting on November 7th, 2015 at London, UK.
Hi Folks,
I am very happy that I will got to #PCM 2015 in London this saturday, I will talk about some of ours Pentaho plugins.
I hope to see all my friends from the Pentaho Community all over the world.
Below there is a copy of Pedro's post about PCM.
It's almost time. #PCM continues it's cruise around Europe. Next stop, for it's 8th year in a row, London.
Here's all the information, taken from the project's Github page (geeks!!)
Pentaho Community Meeting 2015
This page holds all the essential info about the Pentaho Community Meeting 2015.Most important bits first:
- Location: London
- Date: November 7th - there will also be a Hackathon on Friday evening and social activities on Sunday.
- Venue: W12 Conferences, West London
Registration
Attending the presentations and hackathon is completely free!Please register for the main event here for a free ticket.
For the hackathon on Friday evening please register here.
Costs
- As with previous PCM meetings there will be a nominal charge to cover lunch on Saturday.
Agenda
Rough outline, details TBC:- Friday: Evening Hackathon in the city with fancy prizes (courtessy of IVY-IS) to be won, then drinks!
- Saturday: 2 streams of talks - Business and Tech focussed
- Saturday Evening Dinner/drinks around Piccadilly Circys
- Sunday: The sightseeing tour all sightseeing tours should be like. Not to be missed.
How to submit the talks
Please send details to pentaho.community.meetup.2015@gmail.com.Provide the following:
- Your full name
- Links to your profie and company
- Title of the talk and synopsis
Friday: Venue Info, Agenda Etc
Venue Location
Skillsmatter "CodeNode" How to get thereTime - TBC - Evening, which hackathon starting by 7pm, possibly other events occurring before.
Agenda
Saturday: Venue Info, Agenda Etc
Venue Location
W12 Conferences, West London.Address:
W12 Conferences, Artillery Lane, 150 Du Cane Road, London, W12 0HS
How to Get There
Please visit Transport for London for best directions from your London location to W12 Conferences.Nearest tube stations
- Central Line: White City and East Acton both within a 10 minute walk.
- Hammersmith & City and Circle Lines: Wood Lane within a 12 min walk

Buses Buses 7, 70, 72, 272 & 283 bus routes stop directly outside on Du Cane Road. When getting off the bus, look for Queen Charlottes hospital, to your left when looking at Hammersmith Hospital. Artillery Lane is the road running past this towards the car park. Follow this road and turn right at the mini roundabout, then turn left directly into the W12 courtyard, our reception is here.
Nearest Mainline Train stations Paddington Station - 10 mins Take Hammersmith & City or Circle line to Wood Lane Tube station
Liverpool Street – 25 mins Take Central Line to White City station
Victoria Station – 22 mins Take Victoria Line to Oxford Circus. Change to Central Line to White City station.
Kings Cross/St Pancras – 25 mins Take Hammersmith & City or Circle line to Wood Lane Tube station
IMPORTANT: The conference centre is part of the Hospital. YOU MUST NOT ENTER via the main hospital entrance. There is a road between the Prison and Hospital which will take you to conference centre:

Social Media
Twitter hashtag: #pcm15Talks so far (List will evolve!)
Keynotes
- Pentaho 6.0 product roadmap
- Bob Kemper (Executive VP of Engineering): Will discuss the impact of the Hitachi - Pentaho deal on Pentaho and the community
- Pedro Alves: cTools roadmap / community update
Tech Stream
- Matt Casters, Pentaho Chief of Data Integration / Kettle project founder: Data Sets and Unit Tests PDI plugin
- Tom Barber of Meteorite BI will talk about Saiku and managing metadata in a NoSQL world
- Caio Moreno de Souza: Monitoring the BI Pentaho Server using Pentaho CE Audit and Performance Monitoring Plugin / Creating Maps with Saiku Chart Plus
Will Gorman - Pentaho Chief Architect will present something exciting!- Antonio García-Domínguez and Inmaculada Medina-Bulo: ArtifactCatalog: Better Descriptions and Hierarchical Tagging for Pentaho Resources
- Roland Bouman: Will talk about PHASE (Pentaho Analysis Editor) and PASH (Pentaho Analysis Shell).
- Miguel Cunhal: Will present 15-20 top tips and tricks for PDI
- Sébastian Jelsch: Bigdata MDX with Mondrian and Apache Kylin
- Pedro Vale (Webdetails): All the secrets behind Pentaho 6.0
- Jens Bleuel: Everything you wanted to know about PDI 6.0
- Know BI: Metadata injection driven map-reduce
- Diogo Mariano (Webdetails): How to easily embed your cTools dashboard in your web application
- Julio Costa (Webdetails): Responsive design with cTools
- Francesco Corti and Alberto Mercati: transparent and trusted authentication between an external application and Pentaho. (If you've not seen Francescos presentations before you're in for a treat!)
- Marc Batchelor (founder and VP of Engineering Pentaho): Community Contribution Guidelines and Process – How can the community contribute to Pentaho Development
- Andre Simoes (XpandIT: Taming Big Data - Big data is getting mature, is your company ready to handle capture and orchestrate all the processes running within a cluster?
Business Stream
Nelson Sousa of Ubiquis Consulting will talk about Mapping and the benefits it can provide to the business- Owen Bowden Beating blood cancer with help from the Pentaho community
- Mark Stubbs Pentaho Solutions Architect will talk about some of the most exciting Pentaho BigData projects currently running in London
- Juanjo Ortilles Web Adhoc Query Executor (WAQE) A successor to WAQR.
- Emilio Arias Analyzing Ashley Madison data with Pentaho
- Marcello Pontes from oncase Customizing biserver with Tapa and some more plugin goodies. How to take advantage of the plugin whats reusable ans some more hot news for Dashboarders.
Sunday: Venue info, agenda, etc.
Location: central London
Agenda: the London sightseeing tour you wish all sightseeing tours would be like.
A guided tour of London not to be missed. Only 30 spots available, pre-registration required when you sign-in to the conference on Saturday.Will last 2 hours approximately, covering the City of London and surrounding areas.
Hotels
Below are a few hotel suggestions.Please note London is a very large city and commuting may be time consuming. We suggest you choose a hotel either close to the conference venue (Acton, White City, Sheperd's Bush) or closer to the social even on Saturday night (Covent Garden, Soho, Charing Cross).
London Underground is expected to start a 24 hour service during the fall on week-ends. The announced date was September 12, but the recent Tube strikes have pushed this back and there is no official date for commencement of the 24 service yet.
Central London
These hotels are close to the social events on Saturday night, but expect around 30 minutes to get to the conference venue on Saturday:- Travelodge Covent Garden: https://www.travelodge.co.uk/hotels/318/London-Central-Covent-Garden-hotel
- The Z Hotel Soho: http://www.booking.com/hotel/gb/the-z-hotels-soho.en-gb.html
- The Bloomsbury Hotel: http://www.booking.com/hotel/gb/the-bloomsbury.en-gb.html
- Cheshire Hotel: http://www.booking.com/hotel/gb/cheshirehotel.en-gb.html
- Holiday Inn London Mayfair: http://www.booking.com/hotel/gb/holiday-inn-london-mayfair.en-gb.html
Acton/White City
Closer to the conference venue. They are located in zone 2 of the London transporation zone, about 15-20 minutes from Central London- Holiday Inn Express Park Royal (next to North Acton central line tube station): http://www.booking.com/hotel/gb/exhiparkroyal.en-gb.html
- Westfield Apartments (next to White City tube station): http://www.booking.com/hotel/gb/26-white-city-close.en-gb.html
See you there!
Source:
40% of Top 5 Data Scientist from Kaggle are Brazilians.
Hi Folks,
I took a snapshot today of The Kaggle Rankings and 40% of the Top 5 Best Data Scientist are Brazilians.
Kaggle Rankings Stats:
Top 5
2 from Brazil
1 from USA
1 from Grece
1 from Russia
Top 10
4 from Russia
2 from Brazil
1 from Spain
1 from Germany
1 from Greece
1 from USA
I took a snapshot today of The Kaggle Rankings and 40% of the Top 5 Best Data Scientist are Brazilians.
Kaggle Rankings Stats:
Top 5
2 from Brazil
1 from USA
1 from Grece
1 from Russia
Top 10
4 from Russia
2 from Brazil
1 from Spain
1 from Germany
1 from Greece
1 from USA
Thursday, October 29, 2015
Curso de Pentaho + Docker
Baseado na experiência de mais de 2 anos utilizando o Docker com o Pentaho em grandes clientes, lançamos um curso único e pioneiro no Brasil chamado de Curso de Pentaho + Docker.
Durante o curso o aluno aprenderá como utilizar o Docker para criar um projeto de BI com o Pentaho totalmente automático.
O curso tem duração de 12 horas.
Ementa:
Para maiores informações envie um e-mail para info@it4biz.com.br.
Durante o curso o aluno aprenderá como utilizar o Docker para criar um projeto de BI com o Pentaho totalmente automático.
O curso tem duração de 12 horas.
Ementa:
- Introdução ao Docker;
- Introdução ao Docker Compose;
- Introdução ao Docker Hub;
- Introdução ao Github;
- Introdução a Amazon AWS e serviços necessários para um projeto de BI automatizado;
- Criando um primeiro projeto automático utilizando o Docker;
- Passo a Passo de como realizar a automatização de um projeto real feito no Pentaho para funcionar no Docker;
- Deploy de um projeto real na Amazon AWS utilizando o Docker;
- Explicação detalhada do Projeto Real e Open Source - Projeto EDW CENIPA.
Para maiores informações envie um e-mail para info@it4biz.com.br.
Marcadores:
Curso de Pentaho + Docker
Saturday, October 24, 2015
Norse – Superior Attack Intelligence
Norse maintains the world’s largest dedicated threat intelligence network. With over eight million sensors that emulate over six thousand applications – from Apple laptops, to ATM machines, to critical infrastructure systems, to closed-circuit TV cameras - the Norse Intelligence Network gathers data on who the attackers are and what they’re after. Norse delivers that data through the Norse Appliance, which pre-emptively blocks attacks and improves your overall security ROI, and the Norse Intelligence Service, which provides professional continuous threat monitoring for large networks.
Source:
http://map.norsecorp.com
Marcadores:
Norse – Superior Attack Intelligence
Saturday, October 17, 2015
Pentaho Community Meeting 2015 - London
Marcadores:
Pentaho Community Meeting 2015 - London
Thursday, October 15, 2015
Origin of Kettle (PDI - Pentaho Data Integration)
In this video you will have the opportunity to learn about the Origin of Kettle (PDI - Pentaho Data Integration) told by Kettle creator Mr. Matt Casters at Pentaho Day 2014 on May, 16, 2014 in FEA/USP (School of Economics, Business and Accounting of the University of São Paulo).
Link to the video:
Friday, October 09, 2015
Using machine learning and AI to reduce hospital readmissions
Humanoid Robots Future Is Here - 2014 Full Documentary
Tuesday, September 22, 2015
You can live your dream! “No Matter How Bad It Is Or How Bad It Gets, I’m Going To Make It”
Monday, September 21, 2015
Microsoft has Built its own Linux Operating System
Steve Jobs: The Man In The Machine - Official Trailer
How to go to Google Campus Madrid by car, metro or bike
Hi Geek folks from Madrid or anywhere in the world,
Do you want to go to Google Campus Madrid?
Google Campus Madrid
Website: https://www.campus.co/madrid/en
Address: Calle Moreno Nieto, 2 28005 Madrid, Spain
Hours: Monday-Friday 9am-7pm
By car
In the beginning I was coming to Google Campus Madrid by car, but it is probably the worst way to come and the reason is that you can not park here for more than 4 hours.
So you will have to park your car in the streets close to Google Campus and pay about 7 euros per 4 hours and after 4 hours you will have to stay 2 hours away from the district so that way you can come again and park for more 4 hours.
So, by car you will pay about 14 euros to park and you will have all the inconvinient of having to take off your car every 4 hours.
To come by car just in waze or your favorite GPS the street name Calle Moreno Nieto, 2, Madrid.
There are always places to park and it very easy to park anywhere.
By Metro
I do not know why, but Google is in a place "very" far away from a metro station for Madrid standards.
It means you will have to walk about 1 km from the metro station to Google Campus.
In fact, there are a lot of options to come here by metro, but they are all far away.
I already tried two options until now, see it below:
Puerta del Ángel
The best way to go home If you do not want to go up in the hill to Opera.
Opera Metro Station
You can walk from Opera Station to Google Campus.
It is a good option when you are going to Google, because it is all going down by a hill from the Madrid Palace to Google. I will not try to do this to go back home just If I was trying to do some exercise.
By Bike
I came once from my house to Google Campus, it was 10km by bike and it was preety good, but the bad thing is that there is no place to park the bikes inside. They said that they will let everybody park the bike inside even if you are not a resident.
I liked this way a lot and I hope they let us park here without having to pay for it as a resident.
Why did I write this post?
I did it for me, for all my friends that are asking me about Google Campus and maybe for you that are reading it.
I have a bad memory, so I decided to write this post to remember. I do not come here everyday, and even every week or even every months, so it is easy to forget how to come here.
Why Google Campus Madrid?
Google Campus Madrid is a excellent place to work, meet friends, make new friends, learn, make business contacts, study, eat or anything. It is kind of a Starbucks but dedicated to geeks, entrepreneurs and tech guys.
If you come to Google Campus Madrid you will enjoy this international environment, this startup spirit, the amazing internet, the amazing facility, in fact if you are a geek you will feel home.
The problem is that after you start working at Google Campus Madrid you will have difficult to work in others place. Here is just amazing and I wish I could come here everyday.
Working anywhere
I usually work anywhere. When I mean anywhere, that's true. I work anywhere in the world. I travel a lot to a lot of countries and cities and it is very cool to be able to work anywhere.
I work in my client's offices, at the University, at the Metro, the Mall, in the bus, in the car, in the taxi, in the airplane, at home, in my company office in Sao Paulo or Madrid, in the park, at Starbucks and since Google Campus Madrid opened sometimes I will also come here to work and I love it.
If you want to have freedom, you have to learn how to work anywhere and make it productivity.
Do you want to go to Google Campus Madrid?
Google Campus Madrid
Website: https://www.campus.co/madrid/en
Address: Calle Moreno Nieto, 2 28005 Madrid, Spain
Hours: Monday-Friday 9am-7pm
By car
In the beginning I was coming to Google Campus Madrid by car, but it is probably the worst way to come and the reason is that you can not park here for more than 4 hours.
So you will have to park your car in the streets close to Google Campus and pay about 7 euros per 4 hours and after 4 hours you will have to stay 2 hours away from the district so that way you can come again and park for more 4 hours.
So, by car you will pay about 14 euros to park and you will have all the inconvinient of having to take off your car every 4 hours.
To come by car just in waze or your favorite GPS the street name Calle Moreno Nieto, 2, Madrid.
There are always places to park and it very easy to park anywhere.
By Metro
I do not know why, but Google is in a place "very" far away from a metro station for Madrid standards.
It means you will have to walk about 1 km from the metro station to Google Campus.
In fact, there are a lot of options to come here by metro, but they are all far away.
I already tried two options until now, see it below:
Puerta del Ángel
The best way to go home If you do not want to go up in the hill to Opera.
Opera Metro Station
You can walk from Opera Station to Google Campus.
It is a good option when you are going to Google, because it is all going down by a hill from the Madrid Palace to Google. I will not try to do this to go back home just If I was trying to do some exercise.
By Bike
I came once from my house to Google Campus, it was 10km by bike and it was preety good, but the bad thing is that there is no place to park the bikes inside. They said that they will let everybody park the bike inside even if you are not a resident.
I liked this way a lot and I hope they let us park here without having to pay for it as a resident.
Why did I write this post?
I did it for me, for all my friends that are asking me about Google Campus and maybe for you that are reading it.
I have a bad memory, so I decided to write this post to remember. I do not come here everyday, and even every week or even every months, so it is easy to forget how to come here.
Why Google Campus Madrid?
Google Campus Madrid is a excellent place to work, meet friends, make new friends, learn, make business contacts, study, eat or anything. It is kind of a Starbucks but dedicated to geeks, entrepreneurs and tech guys.
If you come to Google Campus Madrid you will enjoy this international environment, this startup spirit, the amazing internet, the amazing facility, in fact if you are a geek you will feel home.
The problem is that after you start working at Google Campus Madrid you will have difficult to work in others place. Here is just amazing and I wish I could come here everyday.
Working anywhere
I usually work anywhere. When I mean anywhere, that's true. I work anywhere in the world. I travel a lot to a lot of countries and cities and it is very cool to be able to work anywhere.
I work in my client's offices, at the University, at the Metro, the Mall, in the bus, in the car, in the taxi, in the airplane, at home, in my company office in Sao Paulo or Madrid, in the park, at Starbucks and since Google Campus Madrid opened sometimes I will also come here to work and I love it.
If you want to have freedom, you have to learn how to work anywhere and make it productivity.
Marcadores:
How to go to Google Campus Madrid by car,
metro or bike
A rich life with less stuff | The Minimalists | TEDxWhitefish
P.W. Singer: Military robots and the future of war
Vijay Kumar: Robots that fly ... and cooperate
Marcadores:
Vijay Kumar: Robots that fly ... and cooperate
Robin Murphy: These robots come to the rescue after a disaster
Larry Page: Where’s Google going next?
Marcadores:
Larry Page: Where’s Google going next?
Friday, September 11, 2015
Big Data A to Z: A glossary of Big Data terminology
This is almost a complete glossary of Big Data terminology widely used today. Let us know if you would like to add any big data terminology missing in this list.
ACID test
A test applied to data for atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability
Aggregation
A process of searching, gathering and presenting data
Algorithm
A mathematical formula placed in software that performs an analysis on a set of data.
Anonymization
The severing of links between people in a database and their records to prevent the discovery of the source of the records.
Artificial Intelligence
Developing intelligence machines and software that are capable of perceiving the environment and take corresponding action when required and even learn from those actions.
Automatic identification and capture (AIDC)
Any method of automatically identifying and collecting data on items, and then storing the data in a computer system. For example, a scanner might collect data about a product being shipped via an RFID chip.
Avro
Avro is a data serialization system that allows for encoding the schema of Hadoop files. It is adept at parsing data and performing remote procedure calls
Behavioral analytics
Using data about people’s behavior to understand intent and predict future actions.
Big Data Scientist
Someone who is able to develop the algorithms to make sense out of big data.
Business Intelligence (BI)
The general term used for the identification, extraction, and analysis of data.
Cascading
Cascading provides a higher level of abstraction for Hadoop, allowing developers to create complex jobs quickly, easily, and in several different languages that run in the JVM, including Ruby, Scala, and more. In effect, this has shattered the skills barrier, enabling Twitter to use Hadoop more broadly.
Call Detail Record (CDR) analysis
CDRs contain data that a telecommunications company collects about phone calls, such as time and length of call. This data can be used in any number of analytical applications.
Cassandra
Cassandra is a distributed and Open Source database. Designed to handle large amounts of distributed data across commodity servers while providing a highly available service. It is a NoSQL solution that was initially developed by Facebook. It is structured in the form of key-value.
Cell phone data
Cell phones generate a tremendous amount of data, and much of it is available for use with analytical applications.
Clickstream Analytics
The analysis of users’ Web activity through the items they click on a page.
Classification analysis
A systematic process for obtaining important and relevant information about data, also meta data called; data about data.
Cloud computing
A distributed computing system over a network used for storing data off-premises
Clustering analysis
The process of identifying objects that are similar to each other and cluster them in order to understand the differences as well as the similarities within the data.
Cold data storage
Storing old data that is hardly used on low-power servers. Retrieving the data will take longer
Comparative analysis
It ensures a step-by-step procedure of comparisons and calculations to detect patterns within very large data sets.
Chukwa
Chukwa is a Hadoop subproject devoted to large-scale log collection and analysis. Chukwa is built on top of the Hadoop distributed filesystem (HDFS) and MapReduce framework and inherits Hadoop’s scalability and robustness. Chukwa also includes a flexible and powerful toolkit for displaying monitoring and analyzing results, in order to make the best use of this collected data.
Clojure
Clojure is a dynamic programming language based on LISP that uses the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). It is well suited for parallel data processing.
Cloud
A broad term that refers to any Internet-based application or service that is hosted remotely.
Columnar database or column-oriented database
A database that stores data by column rather than by row. In a row-based database, a row might contain a name, address, and phone number. In a column-oriented database, all names are in one column, addresses in another, and so on. A key advantage of a columnar database is faster hard disk access.
Comparators
Two ways you may compare your keys is by implementing the interface or by implementing the RawComparator interface. In the former approach, you will compare (deserialized) objects, but in the latter approach, you will compare the keys using their corresponding raw bytes.
Complex event processing (CEP)
CEP is the process of monitoring and analyzing all events across an organization’s systems and acting on them when necessary in real time.
Confabulation
The act of making an intuition-based decision appear to be data-based.
Cross-channel analytics
Analysis that can attribute sales, show average order value, or the lifetime value.
Data access
The act or method of viewing or retrieving stored data.
Dashboard
A graphical representation of the analyses performed by the algorithms
Data aggregation
The act of collecting data from multiple sources for the purpose of reporting or analysis.
Data architecture and design
How enterprise data is structured. The actual structure or design varies depending on the eventual end result required. Data architecture has three stages or processes: conceptual representation of business entities. the logical representation of the relationships among those entities, and the physical construction of the system to support the functionality.
Database
A digital collection of data and the structure around which the data is organized. The data is typically entered into and accessed via a database management system (DBMS).
Database administrator (DBA)
A person, often certified, who is responsible for supporting and maintaining the integrity of the structure and content of a database.
Database as a service (DaaS)
A database hosted in the cloud and sold on a metered basis. Examples include Heroku Postgres and Amazon Relational Database Service.
Database management system (DBMS)
Software that collects and provides access to data in a structured format.
Data center
A physical facility that houses a large number of servers and data storage devices. Data centers might belong to a single organization or sell their services to many organizations.
Data cleansing
The act of reviewing and revising data to remove duplicate entries, correct misspellings, add missing data, and provide more consistency.
Data collection
Any process that captures any type of data.
Data custodian
A person responsible for the database structure and the technical environment, including the storage of data.
Data-directed decision making
Using data to support making crucial decisions.
Data exhaust
The data that a person creates as a byproduct of a common activity–for example, a cell call log or web search history.
Data feed
A means for a person to receive a stream of data. Examples of data feed mechanisms include RSS or Twitter.
Data governance
A set of processes or rules that ensure the integrity of the data and that data management best practices are met.
Data integration
The process of combining data from different sources and presenting it in a single view.
Data integrity
The measure of trust an organization has in the accuracy, completeness, timeliness, and validity of the data.
Data mart
The access layer of a data warehouse used to provide data to users.
Data migration
The process of moving data between different storage types or formats, or between different computer systems.
Data mining
The process of deriving patterns or knowledge from large data sets.
Data model, data modeling
A data model defines the structure of the data for the purpose of communicating between functional and technical people to show data needed for business processes, or for communicating a plan to develop how data is stored and accessed among application development team members.
Data point
An individual item on a graph or a chart.
Data profiling
The process of collecting statistics and information about data in an existing source.
Data quality
The measure of data to determine its worthiness for decision making, planning, or operations.
Data replication
The process of sharing information to ensure consistency between redundant sources.
Data repository
The location of permanently stored data.
Data science
A recent term that has multiple definitions, but generally accepted as a discipline that incorporates statistics, data visualization, computer programming, data mining, machine learning, and database engineering to solve complex problems.
Data scientist
A practitioner of data science.
Data security
The practice of protecting data from destruction or unauthorized access.
Data set
A collection of data, typically in tabular form.
Data source
Any provider of data–for example, a database or a data stream.
Data steward
A person responsible for data stored in a data field.
Data structure
A specific way of storing and organizing data.
Data visualization
A visual abstraction of data designed for the purpose of deriving meaning or communicating information more effectively.
Data warehouse
A place to store data for the purpose of reporting and analysis.
De-identification
The act of removing all data that links a person to a particular piece of information.
Demographic data
Data relating to the characteristics of a human population.
Deep Thunder
IBM’s weather prediction service that provides weather data to organizations such as utilities, which use the data to optimize energy distribution.
Distributed cache
A data cache that is spread across multiple systems but works as one. It is used to improve performance.
Distributed object
A software module designed to work with other distributed objects stored on other computers.
Distributed processing
The execution of a process across multiple computers connected by a computer network.
Distributed File System
Systems that offer simplified, highly available access to storing, analysing and processing data
Document Store Databases
A document-oriented database that is especially designed to store, manage and retrieve documents, also known as semi structured data.
Document management
The practice of tracking and storing electronic documents and scanned images of paper documents.
Drill
An open source distributed system for performing interactive analysis on large-scale datasets. It is similar to Google’s Dremel, and is managed by Apache.
Elasticsearch
An open source search engine built on Apache Lucene.
Event analytics
Shows the series of steps that led to an action.
Exabyte
One million terabytes, or 1 billion gigabytes of information.
External data
Data that exists outside of a system.
Extract, transform, and load (ETL)
A process used in data warehousing to prepare data for use in reporting or analytics.
Exploratory analysis
Finding patterns within data without standard procedures or methods. It is a means of discovering the data and to find the data sets main characteristics.
Failover
The automatic switching to another computer or node should one fail.
Flume
Flume is a framework for populating Hadoop with data. Agents are populated throughout ones IT infrastructure – inside web servers, application servers and mobile devices, for example – to collect data and integrate it into Hadoop.
Grid computing
The performing of computing functions using resources from multiple distributed systems. Grid computing typically involves large files and are most often used for multiple applications. The systems that comprise a grid computing network do not have to be similar in design or in the same geographic location.
Graph Databases
They use graph structures (a finite set of ordered pairs or certain entities), with edges, properties and nodes for data storage. It provides index-free adjacency, meaning that every element is directly linked to its neighbour element.
Hadoop
An open source software library project administered by the Apache Software Foundation. Apache defines Hadoop as “a framework that allows for the distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of computers using a simple programming model.”
Hama
Hama is a distributed computing framework based on Bulk Synchronous Parallel computing techniques for massive scientific computations e.g., matrix, graph and network algorithms. It’s a Top Level Project under the Apache Software Foundation.
HANA
A software/hardware in-memory computing platform from SAP designed for high-volume transactions and real-time analytics.
HBase
HBase is a non-relational database that allows for low-latency, quick lookups in Hadoop. It adds transactional capabilities to Hadoop, allowing users to conduct updates, inserts and deletes. EBay and Facebook use HBase heavily
HCatalog
HCatalog is a centralized metadata management and sharing service for Apache Hadoop. It allows for a unified view of all data in Hadoop clusters and allows diverse tools, including Pig and Hive, to process any data elements without needing to know physically where in the cluster the data is stored.
HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System)
HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System) the storage layer of Hadoop, is a distributed, scalable, Java-based file system adept at storing large volumes of unstructured.
Hive
Hive is a Hadoop-based data warehousing-like framework originally developed by Facebook. It allows users to write queries in a SQL-like language called HiveQL, which are then converted to MapReduce. This allows SQL programmers with no MapReduce experience to use the warehouse and makes it easier to integrate with business intelligence and visualization tools such as Microstrategy, Tableau, Revolutions Analytics, etc.
Hue
Hue (Hadoop User Experience) is an open source web-based interface for making it easier to use Apache Hadoop. It features a file browser for HDFS, an Oozie Application for creating workflows and coordinators, a job designer/browser for MapReduce, a Hive and Impala UI, a Shell, a collection of Hadoop API and more.
Impala
Impala (By Cloudera) provides fast, interactive SQL queries directly on your Apache Hadoop data stored in HDFS or HBase using the same metadata, SQL syntax (Hive SQL), ODBC driver and user interface (Hue Beeswax) as Apache Hive. This provides a familiar and unified platform for batch-oriented or real-time queries.
In-database analytics
The integration of data analytics into the data warehouse.
In-memory database
Any database system that relies on memory for data storage.
In-memory data grid (IMDG)
The storage of data in memory across multiple servers for the purpose of greater scalability and faster access or analytics.
Internet of Things
Ordinary devices that are connected to the internet at any time any where via sensors
Kafka
Kafka (developed by LinkedIn) is a distributed publish-subscribe messaging system that offers a solution capable of handling all data flow activity and processing these data on a consumer website. This type of data (page views, searches, and other user actions) are a key ingredient in the current social web.
Key Value Stores
Key value stores allow the application to store its data in a schema-less way. The data could be stored in a datatype of a programming language or an object. Because of this, there is no need for a fixed data model.
KeyValue Databases
They store data with a primary key, a uniquely identifiable record, which makes easy and fast to look up. The data stored in a KeyValue is normally some kind of primitive of the programming language.
Latency
Any delay in a response or delivery of data from one point to another.
Linked data
As described by World Wide Web inventor Time Berners-Lee, “Cherry-picking common attributes or languages to identify connections or relationships between disparate sources of data.”
Load balancing
The process of distributing workload across a computer network or computer cluster to optimize performance.
Location analytics
Location analytics brings mapping and map-driven analytics to enterprise business systems and data warehouses. It allows you to associate geospatial information with datasets.
Location data
Data that describes a geographic location.
Log file
A file that a computer, network, or application creates automatically to record events that occur during operation–for example, the time a file is accessed.
Machine-generated data
Any data that is automatically created from a computer process, application, or other non-human source.
Machine2Machine data
Two or more machines that are communicating with each other
Machine learning
The use of algorithms to allow a computer to analyze data for the purpose of “learning” what action to take when a specific pattern or event occurs.
MapReduce
MapReduce is a software framework that serves as the compute layer of Hadoop. MapReduce jobs are divided into two (obviously named) parts. The “Map” function divides a query into multiple parts and processes data at the node level. The “Reduce” function aggregates the results of the “Map” function to determine the “answer” to the query.
Mashup
The process of combining different datasets within a single application to enhance output–for example, combining demographic data with real estate listings.
Mahout
Mahout is a data mining library. It takes the most popular data mining algorithms for performing clustering, regression testing and statistical modeling and implements them using the Map Reduce model.
Metadata
Data about data; gives information about what the data is about.
MongoDB
MongoDB is a NoSQL database oriented to documents, developed under the open source concept. It saves data structures in JSON documents with a dynamic scheme (called MongoDB BSON format), making the integration of the data in certain applications more easily and quickly.
MPP database
A database optimized to work in a massively parallel processing environment.
Multi-Dimensional Databases
A database optimized for data online analytical processing (OLAP) applications and for data warehousing.
MultiValue Databases
They are a type of NoSQL and multidimensional databases that understand 3 dimensional data directly. They are primarily giant strings that are perfect for manipulating HTML and XML strings directly
Network analysis
Viewing relationships among the nodes in terms of the network or graph theory, meaning analysing connections between nodes in a network and the strength of the ties.
NewSQL
An elegant, well-defined database system that is easier to learn and better than SQL. It is even newer than NoSQL
NoSQL
NoSQL (commonly interpreted as “not only SQL“) is a broad class of database management systems identified by non-adherence to the widely used relational database management system model. NoSQL databases are not built primarily on tables, and generally do not use SQL for data manipulation.
Object Databases
They store data in the form of objects, as used by object-oriented programming. They are different from relational or graph databases and most of them offer a query language that allows object to be found with a declarative programming approach.
Object-based Image Analysis
Analysing digital images can be performed with data from individual pixels, whereas object-based image analysis uses data from a selection of related pixels, called objects or image objects.
Online analytical processing (OLAP)
The process of analyzing multidimensional data using three operations: consolidation (the aggregation of available), drill-down (the ability for users to see the underlying details), and slice and dice (the ability for users to select subsets and view them from different perspectives).
Online transactional processing (OLTP)
The process of providing users with access to large amounts of transactional data in a way that they can derive meaning from it.
OpenDremel
The open source version of Google’s Big Query java code. It is being integrated with Apache Drill.
Open Data Center Alliance (ODCA)
A consortium of global IT organizations whose goal is to speed the migration of cloud computing.
Operational data store (ODS)
A location to gather and store data from multiple sources so that more operations can be performed on it before sending to the data warehouse for reporting.
Oozie
Oozie is a workflow processing system that lets users define a series of jobs written in multiple languages – such as Map Reduce, Pig and Hive — then intelligently link them to one another. Oozie allows users to specify, for example, that a particular query is only to be initiated after specified previous jobs on which it relies for data are completed.
Parallel data analysis
Breaking up an analytical problem into smaller components and running algorithms on each of those components at the same time. Parallel data analysis can occur within the same system or across multiple systems.
Parallel method invocation (PMI)
Allows programming code to call multiple functions in parallel.
Parallel processing
The ability to execute multiple tasks at the same time.
Parallel query
A query that is executed over multiple system threads for faster performance.
Pattern recognition
The classification or labeling of an identified pattern in the machine learning process.
Pentaho
Pentaho offers a suite of open source Business Intelligence (BI) products called Pentaho Business Analytics providing data integration, OLAP services, reporting, dashboarding, data mining and ETL capabilities
Petabyte
One million gigabytes or 1,024 terabytes.
Pig
Pig Latin is a Hadoop-based language developed by Yahoo. It is relatively easy to learn and is adept at very deep, very long data pipelines (a limitation of SQL).
Predictive analytics
Using statistical functions on one or more datasets to predict trends or future events.
Predictive modeling
The process of developing a model that will most likely predict a trend or outcome.
Public data
Public information or data sets that were created with public funding
Query
Asking for information to answer a certain question
Query analysis
The process of analyzing a search query for the purpose of optimizing it for the best possible result.
R
R is a language and environment for statistical computing and graphics. It is a GNU project which is similar to the S language. R provides a wide variety of statistical (linear and nonlinear modelling, classical statistical tests, time-series analysis, classification, clustering, …) and graphical techniques, and is highly extensible.
Re-identification
Combining several data sets to find a certain person within anonymized data
Real-time data
Data that is created, processed, stored, analysed and visualized within milliseconds
Recommendation engine
An algorithm that analyzes a customer’s purchases and actions on an e-commerce site and then uses that data to recommend complementary products.
Reference data
Data that describes an object and its properties. The object may be physical or virtual.
Risk analysis
The application of statistical methods on one or more datasets to determine the likely risk of a project, action, or decision.
Root-cause analysis
The process of determining the main cause of an event or problem.
Routing analysis
Finding the optimized routing using many different variables for a certain means of transport in order to decrease fuel costs and increase efficiency.
Scalability
The ability of a system or process to maintain acceptable performance levels as workload or scope increases.
Schema
The structure that defines the organization of data in a database system.
Search data
Aggregated data about search terms used over time.
Semi-structured data
Data that is not structured by a formal data model, but provides other means of describing the data and hierarchies.
Sentiment analysis
The application of statistical functions on comments people make on the web and through social networks to determine how they feel about a product or company.
Server
A physical or virtual computer that serves requests for a software application and delivers those requests over a network.
Spatial analysis
It refers to analysing spatial data such geographic data or topological data to identify and understand patterns and regularities within data distributed in geographic space.
SQL
A programming language for retrieving data from a relational database
Sqoop
Sqoop is a connectivity tool for moving data from non-Hadoop data stores – such as relational databases and data warehouses – into Hadoop. It allows users to specify the target location inside of Hadoop and instruct Sqoop to move data from Oracle, Teradata or other relational databases to the target.
Storm
Storm is a system of real-time distributed computing, open source and free, born into Twitter. Storm makes it easy to reliably process unstructured data flows in the field of real-time processing, which made Hadoop for batch processing.
Software as a service (SaaS)
Application software that is used over the web by a thin client or web browser. Salesforce is a well-known example of SaaS.
Storage
Any means of storing data persistently.
Storm
An open-source distributed computation system designed for processing multiple data streams in real time.
Structured data
Data that is organized by a predetermined structure.
Structured Query Language (SQL)
A programming language designed specifically to manage and retrieve data from a relational database system.
Text analytics
The application of statistical, linguistic, and machine learning techniques on text-based sources to derive meaning or insight.
Transactional data
Data that changes unpredictably. Examples include accounts payable and receivable data, or data about product shipments.
Thrift
“Thrift is a software framework for scalable cross-language services development. It combines a software stack with a code generation engine to build services that work efficiently and seamlessly between C++, Java, Python, PHP, Ruby, Erlang, Perl, Haskell, C#, Cocoa, Smalltalk, and OCaml.”
Unstructured data
Data that has no identifiable structure–for example, the text of email messages.
Value
All that available data will create a lot of value for organizations, societies and consumers. Big data means big business and every industry will reap the benefits from big data.
Volume
The amount of data, ranging from megabytes to brontobytes
Visualization
A visual abstraction of data designed for the purpose of deriving meaning or communicating information more effectively.
WebHDFS Apache Hadoop
WebHDFS Apache Hadoop provides native libraries for accessing HDFS. However, users prefer to use HDFS remotely over the heavy client side native libraries. For example, some applications need to load data in and out of the cluster, or to externally interact with the HDFS data. WebHDFS addresses these issues by providing a fully functional HTTP REST API to access HDFS.
Weather data
Real-time weather data is now widely available for organizations to use in a variety of ways. For example, a logistics company can monitor local weather conditions to optimize the transport of goods. A utility company can adjust energy distribution in real time.
XML Databases
XML Databases allow data to be stored in XML format. XML databases are often linked to document-oriented databases. The data stored in an XML database can be queried, exported and serialized into any format needed.
ZooKeeper
ZooKeeper is a software project of the Apache Software Foundation, a service that provides centralized configuration and open code name registration for large distributed systems. ZooKeeper is a subproject of Hadoop.
Source:
http://bigdata-madesimple.com/big-data-a-to-zz-a-glossary-of-big-data-terminology/
ACID test
A test applied to data for atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability
Aggregation
A process of searching, gathering and presenting data
Algorithm
A mathematical formula placed in software that performs an analysis on a set of data.
Anonymization
The severing of links between people in a database and their records to prevent the discovery of the source of the records.
Artificial Intelligence
Developing intelligence machines and software that are capable of perceiving the environment and take corresponding action when required and even learn from those actions.
Automatic identification and capture (AIDC)
Any method of automatically identifying and collecting data on items, and then storing the data in a computer system. For example, a scanner might collect data about a product being shipped via an RFID chip.
Avro
Avro is a data serialization system that allows for encoding the schema of Hadoop files. It is adept at parsing data and performing remote procedure calls
Behavioral analytics
Using data about people’s behavior to understand intent and predict future actions.
Big Data Scientist
Someone who is able to develop the algorithms to make sense out of big data.
Business Intelligence (BI)
The general term used for the identification, extraction, and analysis of data.
Cascading
Cascading provides a higher level of abstraction for Hadoop, allowing developers to create complex jobs quickly, easily, and in several different languages that run in the JVM, including Ruby, Scala, and more. In effect, this has shattered the skills barrier, enabling Twitter to use Hadoop more broadly.
Call Detail Record (CDR) analysis
CDRs contain data that a telecommunications company collects about phone calls, such as time and length of call. This data can be used in any number of analytical applications.
Cassandra
Cassandra is a distributed and Open Source database. Designed to handle large amounts of distributed data across commodity servers while providing a highly available service. It is a NoSQL solution that was initially developed by Facebook. It is structured in the form of key-value.
Cell phone data
Cell phones generate a tremendous amount of data, and much of it is available for use with analytical applications.
Clickstream Analytics
The analysis of users’ Web activity through the items they click on a page.
Classification analysis
A systematic process for obtaining important and relevant information about data, also meta data called; data about data.
Cloud computing
A distributed computing system over a network used for storing data off-premises
Clustering analysis
The process of identifying objects that are similar to each other and cluster them in order to understand the differences as well as the similarities within the data.
Cold data storage
Storing old data that is hardly used on low-power servers. Retrieving the data will take longer
Comparative analysis
It ensures a step-by-step procedure of comparisons and calculations to detect patterns within very large data sets.
Chukwa
Chukwa is a Hadoop subproject devoted to large-scale log collection and analysis. Chukwa is built on top of the Hadoop distributed filesystem (HDFS) and MapReduce framework and inherits Hadoop’s scalability and robustness. Chukwa also includes a flexible and powerful toolkit for displaying monitoring and analyzing results, in order to make the best use of this collected data.
Clojure
Clojure is a dynamic programming language based on LISP that uses the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). It is well suited for parallel data processing.
Cloud
A broad term that refers to any Internet-based application or service that is hosted remotely.
Columnar database or column-oriented database
A database that stores data by column rather than by row. In a row-based database, a row might contain a name, address, and phone number. In a column-oriented database, all names are in one column, addresses in another, and so on. A key advantage of a columnar database is faster hard disk access.
Comparators
Two ways you may compare your keys is by implementing the interface or by implementing the RawComparator interface. In the former approach, you will compare (deserialized) objects, but in the latter approach, you will compare the keys using their corresponding raw bytes.
Complex event processing (CEP)
CEP is the process of monitoring and analyzing all events across an organization’s systems and acting on them when necessary in real time.
Confabulation
The act of making an intuition-based decision appear to be data-based.
Cross-channel analytics
Analysis that can attribute sales, show average order value, or the lifetime value.
Data access
The act or method of viewing or retrieving stored data.
Dashboard
A graphical representation of the analyses performed by the algorithms
Data aggregation
The act of collecting data from multiple sources for the purpose of reporting or analysis.
Data architecture and design
How enterprise data is structured. The actual structure or design varies depending on the eventual end result required. Data architecture has three stages or processes: conceptual representation of business entities. the logical representation of the relationships among those entities, and the physical construction of the system to support the functionality.
Database
A digital collection of data and the structure around which the data is organized. The data is typically entered into and accessed via a database management system (DBMS).
Database administrator (DBA)
A person, often certified, who is responsible for supporting and maintaining the integrity of the structure and content of a database.
Database as a service (DaaS)
A database hosted in the cloud and sold on a metered basis. Examples include Heroku Postgres and Amazon Relational Database Service.
Database management system (DBMS)
Software that collects and provides access to data in a structured format.
Data center
A physical facility that houses a large number of servers and data storage devices. Data centers might belong to a single organization or sell their services to many organizations.
Data cleansing
The act of reviewing and revising data to remove duplicate entries, correct misspellings, add missing data, and provide more consistency.
Data collection
Any process that captures any type of data.
Data custodian
A person responsible for the database structure and the technical environment, including the storage of data.
Data-directed decision making
Using data to support making crucial decisions.
Data exhaust
The data that a person creates as a byproduct of a common activity–for example, a cell call log or web search history.
Data feed
A means for a person to receive a stream of data. Examples of data feed mechanisms include RSS or Twitter.
Data governance
A set of processes or rules that ensure the integrity of the data and that data management best practices are met.
Data integration
The process of combining data from different sources and presenting it in a single view.
Data integrity
The measure of trust an organization has in the accuracy, completeness, timeliness, and validity of the data.
Data mart
The access layer of a data warehouse used to provide data to users.
Data migration
The process of moving data between different storage types or formats, or between different computer systems.
Data mining
The process of deriving patterns or knowledge from large data sets.
Data model, data modeling
A data model defines the structure of the data for the purpose of communicating between functional and technical people to show data needed for business processes, or for communicating a plan to develop how data is stored and accessed among application development team members.
Data point
An individual item on a graph or a chart.
Data profiling
The process of collecting statistics and information about data in an existing source.
Data quality
The measure of data to determine its worthiness for decision making, planning, or operations.
Data replication
The process of sharing information to ensure consistency between redundant sources.
Data repository
The location of permanently stored data.
Data science
A recent term that has multiple definitions, but generally accepted as a discipline that incorporates statistics, data visualization, computer programming, data mining, machine learning, and database engineering to solve complex problems.
Data scientist
A practitioner of data science.
Data security
The practice of protecting data from destruction or unauthorized access.
Data set
A collection of data, typically in tabular form.
Data source
Any provider of data–for example, a database or a data stream.
Data steward
A person responsible for data stored in a data field.
Data structure
A specific way of storing and organizing data.
Data visualization
A visual abstraction of data designed for the purpose of deriving meaning or communicating information more effectively.
Data warehouse
A place to store data for the purpose of reporting and analysis.
De-identification
The act of removing all data that links a person to a particular piece of information.
Demographic data
Data relating to the characteristics of a human population.
Deep Thunder
IBM’s weather prediction service that provides weather data to organizations such as utilities, which use the data to optimize energy distribution.
Distributed cache
A data cache that is spread across multiple systems but works as one. It is used to improve performance.
Distributed object
A software module designed to work with other distributed objects stored on other computers.
Distributed processing
The execution of a process across multiple computers connected by a computer network.
Distributed File System
Systems that offer simplified, highly available access to storing, analysing and processing data
Document Store Databases
A document-oriented database that is especially designed to store, manage and retrieve documents, also known as semi structured data.
Document management
The practice of tracking and storing electronic documents and scanned images of paper documents.
Drill
An open source distributed system for performing interactive analysis on large-scale datasets. It is similar to Google’s Dremel, and is managed by Apache.
Elasticsearch
An open source search engine built on Apache Lucene.
Event analytics
Shows the series of steps that led to an action.
Exabyte
One million terabytes, or 1 billion gigabytes of information.
External data
Data that exists outside of a system.
Extract, transform, and load (ETL)
A process used in data warehousing to prepare data for use in reporting or analytics.
Exploratory analysis
Finding patterns within data without standard procedures or methods. It is a means of discovering the data and to find the data sets main characteristics.
Failover
The automatic switching to another computer or node should one fail.
Flume
Flume is a framework for populating Hadoop with data. Agents are populated throughout ones IT infrastructure – inside web servers, application servers and mobile devices, for example – to collect data and integrate it into Hadoop.
Grid computing
The performing of computing functions using resources from multiple distributed systems. Grid computing typically involves large files and are most often used for multiple applications. The systems that comprise a grid computing network do not have to be similar in design or in the same geographic location.
Graph Databases
They use graph structures (a finite set of ordered pairs or certain entities), with edges, properties and nodes for data storage. It provides index-free adjacency, meaning that every element is directly linked to its neighbour element.
Hadoop
An open source software library project administered by the Apache Software Foundation. Apache defines Hadoop as “a framework that allows for the distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of computers using a simple programming model.”
Hama
Hama is a distributed computing framework based on Bulk Synchronous Parallel computing techniques for massive scientific computations e.g., matrix, graph and network algorithms. It’s a Top Level Project under the Apache Software Foundation.
HANA
A software/hardware in-memory computing platform from SAP designed for high-volume transactions and real-time analytics.
HBase
HBase is a non-relational database that allows for low-latency, quick lookups in Hadoop. It adds transactional capabilities to Hadoop, allowing users to conduct updates, inserts and deletes. EBay and Facebook use HBase heavily
HCatalog
HCatalog is a centralized metadata management and sharing service for Apache Hadoop. It allows for a unified view of all data in Hadoop clusters and allows diverse tools, including Pig and Hive, to process any data elements without needing to know physically where in the cluster the data is stored.
HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System)
HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System) the storage layer of Hadoop, is a distributed, scalable, Java-based file system adept at storing large volumes of unstructured.
Hive
Hive is a Hadoop-based data warehousing-like framework originally developed by Facebook. It allows users to write queries in a SQL-like language called HiveQL, which are then converted to MapReduce. This allows SQL programmers with no MapReduce experience to use the warehouse and makes it easier to integrate with business intelligence and visualization tools such as Microstrategy, Tableau, Revolutions Analytics, etc.
Hue
Hue (Hadoop User Experience) is an open source web-based interface for making it easier to use Apache Hadoop. It features a file browser for HDFS, an Oozie Application for creating workflows and coordinators, a job designer/browser for MapReduce, a Hive and Impala UI, a Shell, a collection of Hadoop API and more.
Impala
Impala (By Cloudera) provides fast, interactive SQL queries directly on your Apache Hadoop data stored in HDFS or HBase using the same metadata, SQL syntax (Hive SQL), ODBC driver and user interface (Hue Beeswax) as Apache Hive. This provides a familiar and unified platform for batch-oriented or real-time queries.
In-database analytics
The integration of data analytics into the data warehouse.
In-memory database
Any database system that relies on memory for data storage.
In-memory data grid (IMDG)
The storage of data in memory across multiple servers for the purpose of greater scalability and faster access or analytics.
Internet of Things
Ordinary devices that are connected to the internet at any time any where via sensors
Kafka
Kafka (developed by LinkedIn) is a distributed publish-subscribe messaging system that offers a solution capable of handling all data flow activity and processing these data on a consumer website. This type of data (page views, searches, and other user actions) are a key ingredient in the current social web.
Key Value Stores
Key value stores allow the application to store its data in a schema-less way. The data could be stored in a datatype of a programming language or an object. Because of this, there is no need for a fixed data model.
KeyValue Databases
They store data with a primary key, a uniquely identifiable record, which makes easy and fast to look up. The data stored in a KeyValue is normally some kind of primitive of the programming language.
Latency
Any delay in a response or delivery of data from one point to another.
Linked data
As described by World Wide Web inventor Time Berners-Lee, “Cherry-picking common attributes or languages to identify connections or relationships between disparate sources of data.”
Load balancing
The process of distributing workload across a computer network or computer cluster to optimize performance.
Location analytics
Location analytics brings mapping and map-driven analytics to enterprise business systems and data warehouses. It allows you to associate geospatial information with datasets.
Location data
Data that describes a geographic location.
Log file
A file that a computer, network, or application creates automatically to record events that occur during operation–for example, the time a file is accessed.
Machine-generated data
Any data that is automatically created from a computer process, application, or other non-human source.
Machine2Machine data
Two or more machines that are communicating with each other
Machine learning
The use of algorithms to allow a computer to analyze data for the purpose of “learning” what action to take when a specific pattern or event occurs.
MapReduce
MapReduce is a software framework that serves as the compute layer of Hadoop. MapReduce jobs are divided into two (obviously named) parts. The “Map” function divides a query into multiple parts and processes data at the node level. The “Reduce” function aggregates the results of the “Map” function to determine the “answer” to the query.
Mashup
The process of combining different datasets within a single application to enhance output–for example, combining demographic data with real estate listings.
Mahout
Mahout is a data mining library. It takes the most popular data mining algorithms for performing clustering, regression testing and statistical modeling and implements them using the Map Reduce model.
Metadata
Data about data; gives information about what the data is about.
MongoDB
MongoDB is a NoSQL database oriented to documents, developed under the open source concept. It saves data structures in JSON documents with a dynamic scheme (called MongoDB BSON format), making the integration of the data in certain applications more easily and quickly.
MPP database
A database optimized to work in a massively parallel processing environment.
Multi-Dimensional Databases
A database optimized for data online analytical processing (OLAP) applications and for data warehousing.
MultiValue Databases
They are a type of NoSQL and multidimensional databases that understand 3 dimensional data directly. They are primarily giant strings that are perfect for manipulating HTML and XML strings directly
Network analysis
Viewing relationships among the nodes in terms of the network or graph theory, meaning analysing connections between nodes in a network and the strength of the ties.
NewSQL
An elegant, well-defined database system that is easier to learn and better than SQL. It is even newer than NoSQL
NoSQL
NoSQL (commonly interpreted as “not only SQL“) is a broad class of database management systems identified by non-adherence to the widely used relational database management system model. NoSQL databases are not built primarily on tables, and generally do not use SQL for data manipulation.
Object Databases
They store data in the form of objects, as used by object-oriented programming. They are different from relational or graph databases and most of them offer a query language that allows object to be found with a declarative programming approach.
Object-based Image Analysis
Analysing digital images can be performed with data from individual pixels, whereas object-based image analysis uses data from a selection of related pixels, called objects or image objects.
Online analytical processing (OLAP)
The process of analyzing multidimensional data using three operations: consolidation (the aggregation of available), drill-down (the ability for users to see the underlying details), and slice and dice (the ability for users to select subsets and view them from different perspectives).
Online transactional processing (OLTP)
The process of providing users with access to large amounts of transactional data in a way that they can derive meaning from it.
OpenDremel
The open source version of Google’s Big Query java code. It is being integrated with Apache Drill.
Open Data Center Alliance (ODCA)
A consortium of global IT organizations whose goal is to speed the migration of cloud computing.
Operational data store (ODS)
A location to gather and store data from multiple sources so that more operations can be performed on it before sending to the data warehouse for reporting.
Oozie
Oozie is a workflow processing system that lets users define a series of jobs written in multiple languages – such as Map Reduce, Pig and Hive — then intelligently link them to one another. Oozie allows users to specify, for example, that a particular query is only to be initiated after specified previous jobs on which it relies for data are completed.
Parallel data analysis
Breaking up an analytical problem into smaller components and running algorithms on each of those components at the same time. Parallel data analysis can occur within the same system or across multiple systems.
Parallel method invocation (PMI)
Allows programming code to call multiple functions in parallel.
Parallel processing
The ability to execute multiple tasks at the same time.
Parallel query
A query that is executed over multiple system threads for faster performance.
Pattern recognition
The classification or labeling of an identified pattern in the machine learning process.
Pentaho
Pentaho offers a suite of open source Business Intelligence (BI) products called Pentaho Business Analytics providing data integration, OLAP services, reporting, dashboarding, data mining and ETL capabilities
Petabyte
One million gigabytes or 1,024 terabytes.
Pig
Pig Latin is a Hadoop-based language developed by Yahoo. It is relatively easy to learn and is adept at very deep, very long data pipelines (a limitation of SQL).
Predictive analytics
Using statistical functions on one or more datasets to predict trends or future events.
Predictive modeling
The process of developing a model that will most likely predict a trend or outcome.
Public data
Public information or data sets that were created with public funding
Query
Asking for information to answer a certain question
Query analysis
The process of analyzing a search query for the purpose of optimizing it for the best possible result.
R
R is a language and environment for statistical computing and graphics. It is a GNU project which is similar to the S language. R provides a wide variety of statistical (linear and nonlinear modelling, classical statistical tests, time-series analysis, classification, clustering, …) and graphical techniques, and is highly extensible.
Re-identification
Combining several data sets to find a certain person within anonymized data
Real-time data
Data that is created, processed, stored, analysed and visualized within milliseconds
Recommendation engine
An algorithm that analyzes a customer’s purchases and actions on an e-commerce site and then uses that data to recommend complementary products.
Reference data
Data that describes an object and its properties. The object may be physical or virtual.
Risk analysis
The application of statistical methods on one or more datasets to determine the likely risk of a project, action, or decision.
Root-cause analysis
The process of determining the main cause of an event or problem.
Routing analysis
Finding the optimized routing using many different variables for a certain means of transport in order to decrease fuel costs and increase efficiency.
Scalability
The ability of a system or process to maintain acceptable performance levels as workload or scope increases.
Schema
The structure that defines the organization of data in a database system.
Search data
Aggregated data about search terms used over time.
Semi-structured data
Data that is not structured by a formal data model, but provides other means of describing the data and hierarchies.
Sentiment analysis
The application of statistical functions on comments people make on the web and through social networks to determine how they feel about a product or company.
Server
A physical or virtual computer that serves requests for a software application and delivers those requests over a network.
Spatial analysis
It refers to analysing spatial data such geographic data or topological data to identify and understand patterns and regularities within data distributed in geographic space.
SQL
A programming language for retrieving data from a relational database
Sqoop
Sqoop is a connectivity tool for moving data from non-Hadoop data stores – such as relational databases and data warehouses – into Hadoop. It allows users to specify the target location inside of Hadoop and instruct Sqoop to move data from Oracle, Teradata or other relational databases to the target.
Storm
Storm is a system of real-time distributed computing, open source and free, born into Twitter. Storm makes it easy to reliably process unstructured data flows in the field of real-time processing, which made Hadoop for batch processing.
Software as a service (SaaS)
Application software that is used over the web by a thin client or web browser. Salesforce is a well-known example of SaaS.
Storage
Any means of storing data persistently.
Storm
An open-source distributed computation system designed for processing multiple data streams in real time.
Structured data
Data that is organized by a predetermined structure.
Structured Query Language (SQL)
A programming language designed specifically to manage and retrieve data from a relational database system.
Text analytics
The application of statistical, linguistic, and machine learning techniques on text-based sources to derive meaning or insight.
Transactional data
Data that changes unpredictably. Examples include accounts payable and receivable data, or data about product shipments.
Thrift
“Thrift is a software framework for scalable cross-language services development. It combines a software stack with a code generation engine to build services that work efficiently and seamlessly between C++, Java, Python, PHP, Ruby, Erlang, Perl, Haskell, C#, Cocoa, Smalltalk, and OCaml.”
Unstructured data
Data that has no identifiable structure–for example, the text of email messages.
Value
All that available data will create a lot of value for organizations, societies and consumers. Big data means big business and every industry will reap the benefits from big data.
Volume
The amount of data, ranging from megabytes to brontobytes
Visualization
A visual abstraction of data designed for the purpose of deriving meaning or communicating information more effectively.
WebHDFS Apache Hadoop
WebHDFS Apache Hadoop provides native libraries for accessing HDFS. However, users prefer to use HDFS remotely over the heavy client side native libraries. For example, some applications need to load data in and out of the cluster, or to externally interact with the HDFS data. WebHDFS addresses these issues by providing a fully functional HTTP REST API to access HDFS.
Weather data
Real-time weather data is now widely available for organizations to use in a variety of ways. For example, a logistics company can monitor local weather conditions to optimize the transport of goods. A utility company can adjust energy distribution in real time.
XML Databases
XML Databases allow data to be stored in XML format. XML databases are often linked to document-oriented databases. The data stored in an XML database can be queried, exported and serialized into any format needed.
ZooKeeper
ZooKeeper is a software project of the Apache Software Foundation, a service that provides centralized configuration and open code name registration for large distributed systems. ZooKeeper is a subproject of Hadoop.
Source:
http://bigdata-madesimple.com/big-data-a-to-zz-a-glossary-of-big-data-terminology/
Visão Geral sobre os Mórmons
Visão Geral sobre os MórmonsEste vídeo mostra uma visão geral sobre A Igreja de Jesus Cristo dos Santos dos Últimos Dias. Conheça algumas das crenças básicas e programas dos mórmons.
Posted by A Igreja de Jesus Cristo dos Santos dos Últimos Dias (Oficial) - Notícias on Thursday, June 11, 2015
Marcadores:
Visão Geral sobre os Mórmons
Thursday, September 10, 2015
Encuentro de la Comunidad Pentaho en Madrid, España en el dia 17/09/15
Hola a todos,
En el dia 17 de Septiembre de 2015 a las 19:00hs en la calle Salvatierra, 4, Madrid, 28034 (Open Sistemas) vamos tener un Encuentro de la Comunidad Pentaho en Madrid, España.
Catch up sobre pentaho (#pcm), desarrollos propios y aquitectura y mas cosas.
Agenda
• Presentación de la sesión
• Arquitectura de pentaho en HA
• Desarrollo y funcionamiento de OS-User-Actions.
• Trabajo con enlaces simbólicos de Git y pentaho
• Monitorizando BI Pentaho Server con Pentaho CE Audit y Plugin de monitorización de rendimiento
Link para hacer la inscripción en el evento:
http://www.meetup.com/pt/Grupo-de-usuarios-de-Pentaho-y-Saiku-de-Madrid/events/224030926/
En el dia 17 de Septiembre de 2015 a las 19:00hs en la calle Salvatierra, 4, Madrid, 28034 (Open Sistemas) vamos tener un Encuentro de la Comunidad Pentaho en Madrid, España.
Catch up sobre pentaho (#pcm), desarrollos propios y aquitectura y mas cosas.
Agenda
• Presentación de la sesión
• Arquitectura de pentaho en HA
• Desarrollo y funcionamiento de OS-User-Actions.
• Trabajo con enlaces simbólicos de Git y pentaho
• Monitorizando BI Pentaho Server con Pentaho CE Audit y Plugin de monitorización de rendimiento
Link para hacer la inscripción en el evento:
http://www.meetup.com/pt/Grupo-de-usuarios-de-Pentaho-y-Saiku-de-Madrid/events/224030926/
Saturday, August 29, 2015
Lindo video feito pelo Toddynho sobre a família
Marcadores:
Lindo video feito pelo Toddynho sobre a família
How to install Android Studio on Mac OS X 10.11 (Beta)
Visit the link http://developer.android.com/sdk/installing/index.html?pkg=studio
Installing Android Studio
Android Studio provides everything you need to start developing apps for Android, including the Android Studio IDE and the Android SDK tools.
If you didn't download Android Studio, go download Android Studio now, or switch to the stand-alone SDK Tools install instructions.
Before you set up Android Studio, be sure you have installed JDK 6 or higher (the JRE alone is not sufficient)—JDK 7 is required when developing for Android 5.0 and higher. To check if you have JDK installed (and which version), open a terminal and type javac -version. If the JDK is not available or the version is lower than 6, go download JDK.
[ Show instructions for all platforms ]
To set up Android Studio on Mac OSX:
Launch the .dmg file you just downloaded.
Drag and drop Android Studio into the Applications folder.
Open Android Studio and follow the setup wizard to install any necessary SDK tools.
Depending on your security settings, when you attempt to open Android Studio, you might see a warning that says the package is damaged and should be moved to the trash. If this happens, go to System Preferences > Security & Privacy and under Allow applications downloaded from, select Anywhere. Then open Android Studio again.
If you need use the Android SDK tools from a command line, you can access them at:
/Users//Library/Android/sdk/
Android Studio is now ready and loaded with the Android developer tools, but there are still a couple packages you should add to make your Android SDK complete.
See the screens below to help you understand better the whole process.
Installing Android Studio
Android Studio provides everything you need to start developing apps for Android, including the Android Studio IDE and the Android SDK tools.
If you didn't download Android Studio, go download Android Studio now, or switch to the stand-alone SDK Tools install instructions.
Before you set up Android Studio, be sure you have installed JDK 6 or higher (the JRE alone is not sufficient)—JDK 7 is required when developing for Android 5.0 and higher. To check if you have JDK installed (and which version), open a terminal and type javac -version. If the JDK is not available or the version is lower than 6, go download JDK.
[ Show instructions for all platforms ]
To set up Android Studio on Mac OSX:
Launch the .dmg file you just downloaded.
Drag and drop Android Studio into the Applications folder.
Open Android Studio and follow the setup wizard to install any necessary SDK tools.
Depending on your security settings, when you attempt to open Android Studio, you might see a warning that says the package is damaged and should be moved to the trash. If this happens, go to System Preferences > Security & Privacy and under Allow applications downloaded from, select Anywhere. Then open Android Studio again.
If you need use the Android SDK tools from a command line, you can access them at:
/Users/
Android Studio is now ready and loaded with the Android developer tools, but there are still a couple packages you should add to make your Android SDK complete.
See the screens below to help you understand better the whole process.
Saturday, August 22, 2015
Free and Open Source Easy Reimbursement Platform
If your travels take up much of your agenda, and controlling your travel expenses consume most of the time you have left, do not waste time and experience (Easy Reimbursement) now!
Using a cell phone the user record his/her expenses.
Visit our project webpage at https://github.com/EasyReimbursement
The first free and open source platform about reimbursement management in the World
It is the first free and open source platform about reimbursement management in the World. It was launched officialy on Google Play at March, 8, 2011.
We are the only free and open source reimbursement management platform in the World.
All our components of Easy Reimbursement Platform are open source and free.
Easy Reimbursement Free
Easy Reimbursement Free is an Android app to help people to manage their travel expensives.
Download it from Google PlayThe link is https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=br.com.reembolsofacil.free&hl=en
Learn more about it:
Visit the link:
http://pt.slideshare.net/caiomsouza/apresentao-reembolso-fcil
http://reembolsofacil.blogspot.com.br
Reembolso Facil at Globo.com | Tech Tudo
http://www.techtudo.com.br/tudo-sobre/reembolso-facil.html
Reembolso Fácil Twitter:https://twitter.com/reembolsofacil
Credits:
Caio Moreno de Souza (twitter: @caiomsouza)
Fausto Koga
Marcadores:
Free and Open Source Easy Reimbursement Platform
Monday, August 10, 2015
Slidify Demo
http://ramnathv.github.io/slidify/
Marcadores:
Slidify Demo
Friday, August 07, 2015
Deep learning - Yann LeCun, à l'USI
Marcadores:
à l'USI,
Deep learning - Yann LeCun
Peter Norvig, Google - Stanford Big Data 2015
Marcadores:
Google - Stanford Big Data 2015,
Peter Norvig
The Future of Data Science - Data Science @ Stanford
Sunday, August 02, 2015
You Should Learn to Program: Christian Genco at TEDxSMU
Tuesday, July 21, 2015
DOWNLOAD: 523.50Mb/s | UPLOAD: 429.97Mb/s | PING 33 ms
Tuesday, July 14, 2015
Logstash | Collect, Enrich & Transport Data
Logstash is a tool for managing events and logs. You can use it to collect
logs, parse them, and store them for later use (like, for searching). If you
store them in Elasticsearch,
you can view and analyze them with Kibana.
It is fully free and fully open source. The license is Apache 2.0, meaning you are pretty much free to use it however you want in whatever way.
For more info, see https://www.elastic.co/products/logstash
https://www.elastic.co/products/logstash
https://github.com/elastic/logstash
http://hemingway.softwarelivre.org/fisl16/high/41e/sala_41e-high-201507101700.ogv
http://jasonwilder.com/blog/2013/11/19/fluentd-vs-logstash/
It is fully free and fully open source. The license is Apache 2.0, meaning you are pretty much free to use it however you want in whatever way.
For more info, see https://www.elastic.co/products/logstash
https://www.elastic.co/products/logstash
https://github.com/elastic/logstash
http://hemingway.softwarelivre.org/fisl16/high/41e/sala_41e-high-201507101700.ogv
http://jasonwilder.com/blog/2013/11/19/fluentd-vs-logstash/
Marcadores:
Logstash
Monday, July 13, 2015
Telefonica Smart Steps
Smart Steps is an Insights solution that uses anonymous and aggregated mobile data to help organizations make better business decisions based on actual behaviour.
http://dynamicinsights.telefonica.com/blog/488/smart-steps-2
http://dynamicinsights.telefonica.com/blog/488/smart-steps-2
Marcadores:
Telefonica Smart Steps
Saturday, July 11, 2015
An Interactive Introduction To R (Programming Language For Statistics)
Saturday, July 04, 2015
Dunbar's number x Our Facebook "Friends/connections"
How can we have so many "Friends" on Facebook?
Are they really our "friends" or just connections like we have in LinkedIn, twitter or others social networks?
Read the text below and think about it.
Dunbar's number
Dunbar's number is a suggested cognitive limit to the number of people with whom one can maintain stable social relationships. These are relationships in which an individual knows who each person is and how each person relates to every other person.[1][2][3][4][5][6] This number was first proposed in the 1990s by British anthropologist Robin Dunbar, who found a correlation between primate brain size and average social group size.[7] By using the average human brain size and extrapolating from the results of primates, he proposed that humans can only comfortably maintain 150 stable relationships.[8] Proponents assert that numbers larger than this generally require more restrictive rules, laws, and enforced norms to maintain a stable, cohesive group. It has been proposed to lie between 100 and 250, with a commonly used value of 150.[9][10] Dunbar's number states the number of people one knows and keeps social contact with, and it does not include the number of people known personally with a ceased social relationship, nor people just generally known with a lack of persistent social relationship, a number which might be much higher and likely depends on long-term memory size.
Dunbar theorized that "this limit is a direct function of relative neocortex size, and that this in turn limits group size ... the limit imposed by neocortical processing capacity is simply on the number of individuals with whom a stable inter-personal relationship can be maintained." On the periphery, the number also includes past colleagues, such as high school friends, with whom a person would want to reacquaint themself if they met again.[11]
Source:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dunbar's_number
Are they really our "friends" or just connections like we have in LinkedIn, twitter or others social networks?
Read the text below and think about it.
Dunbar's number
Dunbar's number is a suggested cognitive limit to the number of people with whom one can maintain stable social relationships. These are relationships in which an individual knows who each person is and how each person relates to every other person.[1][2][3][4][5][6] This number was first proposed in the 1990s by British anthropologist Robin Dunbar, who found a correlation between primate brain size and average social group size.[7] By using the average human brain size and extrapolating from the results of primates, he proposed that humans can only comfortably maintain 150 stable relationships.[8] Proponents assert that numbers larger than this generally require more restrictive rules, laws, and enforced norms to maintain a stable, cohesive group. It has been proposed to lie between 100 and 250, with a commonly used value of 150.[9][10] Dunbar's number states the number of people one knows and keeps social contact with, and it does not include the number of people known personally with a ceased social relationship, nor people just generally known with a lack of persistent social relationship, a number which might be much higher and likely depends on long-term memory size.
Dunbar theorized that "this limit is a direct function of relative neocortex size, and that this in turn limits group size ... the limit imposed by neocortical processing capacity is simply on the number of individuals with whom a stable inter-personal relationship can be maintained." On the periphery, the number also includes past colleagues, such as high school friends, with whom a person would want to reacquaint themself if they met again.[11]
Source:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dunbar's_number
Tuesday, June 30, 2015
Saturday, June 27, 2015
How to install GitBook using NPM
Visit the website: https://github.com/GitbookIO/gitbook
Type on your terminal:
npm install gitbook-cli -g
output:
Caios-MacBook-Pro:thedatasciencenotebook caiomsouza$ npm install gitbook-cli -g
/usr/local/bin/gitbook -> /usr/local/lib/node_modules/gitbook-cli/bin/gitbook.js
gitbook-cli@0.3.4 /usr/local/lib/node_modules/gitbook-cli
├── bash-color@0.0.3
├── user-home@1.1.1
├── commander@2.6.0
├── tmp@0.0.23
├── q@1.0.1
├── semver@2.2.1
├── lodash@2.4.1
├── npmi@0.1.1 (semver@4.3.6)
├── optimist@0.6.1 (wordwrap@0.0.3, minimist@0.0.10)
├── npm@2.4.1
└── fs-extra@0.15.0 (jsonfile@2.2.1, graceful-fs@3.0.8, rimraf@2.4.0)
Type on your terminal:
npm install gitbook-cli -g
output:
Caios-MacBook-Pro:thedatasciencenotebook caiomsouza$ npm install gitbook-cli -g
/usr/local/bin/gitbook -> /usr/local/lib/node_modules/gitbook-cli/bin/gitbook.js
gitbook-cli@0.3.4 /usr/local/lib/node_modules/gitbook-cli
├── bash-color@0.0.3
├── user-home@1.1.1
├── commander@2.6.0
├── tmp@0.0.23
├── q@1.0.1
├── semver@2.2.1
├── lodash@2.4.1
├── npmi@0.1.1 (semver@4.3.6)
├── optimist@0.6.1 (wordwrap@0.0.3, minimist@0.0.10)
├── npm@2.4.1
└── fs-extra@0.15.0 (jsonfile@2.2.1, graceful-fs@3.0.8, rimraf@2.4.0)
Marcadores:
How to install GitBook using NPM
How to Install Node.js and NPM on a Mac
Visit the website: http://blog.teamtreehouse.com/install-node-js-npm-mac
Type on your terminal:
brew install node
output:
Caios-MacBook-Pro:thedatasciencenotebook caiomsouza$ brew install node
==> Downloading https://homebrew.bintray.com/bottles/node-0.12.5.yosemite.bottle.tar.gz
######################################################################## 100.0%
==> Pouring node-0.12.5.yosemite.bottle.tar.gz
==> Caveats
Bash completion has been installed to:
/usr/local/etc/bash_completion.d
==> Summary
🍺 /usr/local/Cellar/node/0.12.5: 2681 files, 29M
Caios-MacBook-Pro:thedatasciencenotebook caiomsouza$ node -v
v0.12.5
Caios-MacBook-Pro:thedatasciencenotebook caiomsouza$ npm -v
2.11.2
Type on your terminal:
brew install node
output:
Caios-MacBook-Pro:thedatasciencenotebook caiomsouza$ brew install node
==> Downloading https://homebrew.bintray.com/bottles/node-0.12.5.yosemite.bottle.tar.gz
######################################################################## 100.0%
==> Pouring node-0.12.5.yosemite.bottle.tar.gz
==> Caveats
Bash completion has been installed to:
/usr/local/etc/bash_completion.d
==> Summary
🍺 /usr/local/Cellar/node/0.12.5: 2681 files, 29M
Caios-MacBook-Pro:thedatasciencenotebook caiomsouza$ node -v
v0.12.5
Caios-MacBook-Pro:thedatasciencenotebook caiomsouza$ npm -v
2.11.2
Marcadores:
How to Install Node.js and NPM on a Mac
How to Install Homebrew on Mac OS
Read the website http://brew.sh
Type on your terminal:
ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"
output:
Caios-MacBook-Pro:thedatasciencenotebook caiomsouza$ ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"
==> This script will install:
/usr/local/bin/brew
/usr/local/Library/...
/usr/local/share/man/man1/brew.1
==> The following directories will be made group writable:
/usr/local/.
/usr/local/include
/usr/local/lib
/usr/local/lib/pkgconfig
/usr/local/share
/usr/local/share/man
/usr/local/share/man/man1
==> The following directories will have their group set to admin:
/usr/local/.
/usr/local/include
/usr/local/lib
/usr/local/lib/pkgconfig
/usr/local/share
/usr/local/share/man
/usr/local/share/man/man1
Press RETURN to continue or any other key to abort
==> /usr/bin/sudo /bin/chmod g+rwx /usr/local/. /usr/local/include /usr/local/lib /usr/local/lib/pkgconfig /usr/local/share /usr/local/share/man /usr/local/share/man/man1
Password:
==> /usr/bin/sudo /usr/bin/chgrp admin /usr/local/. /usr/local/include /usr/local/lib /usr/local/lib/pkgconfig /usr/local/share /usr/local/share/man /usr/local/share/man/man1
==> /usr/bin/sudo /bin/mkdir /Library/Caches/Homebrew
==> /usr/bin/sudo /bin/chmod g+rwx /Library/Caches/Homebrew
==> Downloading and installing Homebrew...
remote: Counting objects: 3641, done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (3474/3474), done.
remote: Total 3641 (delta 36), reused 726 (delta 26), pack-reused 0
Receiving objects: 100% (3641/3641), 2.94 MiB | 0 bytes/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (36/36), done.
From https://github.com/Homebrew/homebrew
* [new branch] master -> origin/master
HEAD is now at a1ad7ee dynamips: update homepage
==> Installation successful!
==> Next steps
Run `brew help` to get started
Type on your terminal:
ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"
output:
Caios-MacBook-Pro:thedatasciencenotebook caiomsouza$ ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"
==> This script will install:
/usr/local/bin/brew
/usr/local/Library/...
/usr/local/share/man/man1/brew.1
==> The following directories will be made group writable:
/usr/local/.
/usr/local/include
/usr/local/lib
/usr/local/lib/pkgconfig
/usr/local/share
/usr/local/share/man
/usr/local/share/man/man1
==> The following directories will have their group set to admin:
/usr/local/.
/usr/local/include
/usr/local/lib
/usr/local/lib/pkgconfig
/usr/local/share
/usr/local/share/man
/usr/local/share/man/man1
Press RETURN to continue or any other key to abort
==> /usr/bin/sudo /bin/chmod g+rwx /usr/local/. /usr/local/include /usr/local/lib /usr/local/lib/pkgconfig /usr/local/share /usr/local/share/man /usr/local/share/man/man1
Password:
==> /usr/bin/sudo /usr/bin/chgrp admin /usr/local/. /usr/local/include /usr/local/lib /usr/local/lib/pkgconfig /usr/local/share /usr/local/share/man /usr/local/share/man/man1
==> /usr/bin/sudo /bin/mkdir /Library/Caches/Homebrew
==> /usr/bin/sudo /bin/chmod g+rwx /Library/Caches/Homebrew
==> Downloading and installing Homebrew...
remote: Counting objects: 3641, done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (3474/3474), done.
remote: Total 3641 (delta 36), reused 726 (delta 26), pack-reused 0
Receiving objects: 100% (3641/3641), 2.94 MiB | 0 bytes/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (36/36), done.
From https://github.com/Homebrew/homebrew
* [new branch] master -> origin/master
HEAD is now at a1ad7ee dynamips: update homepage
==> Installation successful!
==> Next steps
Run `brew help` to get started
Marcadores:
How to Install Homebrew on Mac OS
Friday, June 26, 2015
Atom 1.0 - A hackable text editor for the 21st Century
Atom is a text editor that's modern, approachable, yet hackable to the core—a tool you can customize to do anything but also use productively without ever touching a config file.
Monday, June 22, 2015
adminpackage4r - Admin Package For R is an easy way to manage your packages in R
Hi Folks,
This weekend I created Admin Package for R, it is still version 0.1 but maybe it will help you.
This weekend I created Admin Package for R, it is still version 0.1 but maybe it will help you.
# Loadadminpackage4rlibrary("adminpackage4r")
# Specify the list of required packages to be installed and load
Required_Packages=c("ggplot2", "Rcpp", "plyr", "sqldf");
# Call the Function
Install_And_Load(Required_Packages); Source:https://github.com/caiomsouza/adminpackage4r Big Data ¿Navegar o naufragar en un mar de datos?
Friday, June 19, 2015
Kylin integration into Pentahos Business Analytics Platform
Kylin integration into Pentahos Business Analytics Platform
Pre-installation Requirements
See the link below to more details:
https://github.com/mustangore/thesis
Pre-installation Requirements
- Pentahos Business Analytics Platform (Community Edition): 5.2.0.0-209
- Installed Saiku 3.0.9.9 from Marketplace
- Cloudera 5.3 VM with TCP Port-Forwarding from 7071 (Host) to 7070 (Guest)
- Kylin 0.6.4 installed on your VM with at least one successfully built Cube. Kylin has to run on Port 7070. For more information see https://github.com/KylinOLAP/Kylin/wiki/On-Hadoop-CLI-installation
See the link below to more details:
https://github.com/mustangore/thesis
Sunday, June 14, 2015
Build Your Own Drone
If you want to build your own drone, please read it:
http://www.airspacemag.com/flight-today/build-your-own-drone-180951417/?page=1
http://myfirstdrone.com
http://www.airspacemag.com/flight-today/build-your-own-drone-180951417/?page=1
http://myfirstdrone.com
Marcadores:
Build Your Own Drone
Setting Up Your DJI Drone with Naza Assistant Software | Phantom, Naza Flight Controller
How To: Make A Drone (Quadcopter)
Here are the specs of the build:
HJ450 Frame - Black and White Arms (DJI F450 Look Alike) - eBay.com
Naza M-V2 w/ GPS and PMU - eBay.com
Spektrum DX7s 2.4 GHz TX - eBay.com
Spekrtum AR8000 2.4 GHz RX - Came with DX7s TX
Hobby King 30 Amp ESCs - hobbyking.com
Cheetah 2217-08 Motors (1100kV, 200W) - gravesrc.com
http://www.ebay.co.uk/itm/DJI-Flame-Wheel-F450-ARF-Naza-M-Lite-COMBO-w-LED-Module-E300-MOTORS-ESC-Props-l-/281628196583
Marcadores:
How To: Make A Drone (Quadcopter)
Saturday, June 13, 2015
How to install python-louvain 0.3 (Louvain algorithm for community detection) on Mac OS
Install community library:
Louvain algorithm for community detection
1) download from: https://pypi.python.org/pypi/python-louvain/0.3
2) Unzip python-louvain-0.3.tar.gz
3) Run on terminal the command sudo python setup.py install in side the unzip folder called python-louvain-0.3
4) Restart ipython notebook
5) Try it.
Last login: Sat Jun 13 10:25:49 on ttys000
Caios-MacBook-Pro:u-tad caiomsouza$ sudo python setup.py install
Password:
python: can't open file 'setup.py': [Errno 2] No such file or directory
Caios-MacBook-Pro:u-tad caiomsouza$ ls
Mod1 Mod15 Mod5 contributors.txt
Mod10 Mod16 Mod6 material-internet
Mod11 Mod17 Mod7 planning_EDS_2ED.pdf
Mod12 Mod2 Mod8
Mod13 Mod3 Mod9
Mod14 Mod4 actividades-utad.xlsx
Caios-MacBook-Pro:u-tad caiomsouza$ cd Mod9/
Caios-MacBook-Pro:Mod9 caiomsouza$ ls
GD_M09_Grafos_SNA.pdf datasets python-lib slides
Caios-MacBook-Pro:Mod9 caiomsouza$ cd python-lib/
Caios-MacBook-Pro:python-lib caiomsouza$ ls
python-louvain-0.3.tar.gz
Caios-MacBook-Pro:python-lib caiomsouza$ ls
python-louvain-0.3 python-louvain-0.3.tar.gz
Caios-MacBook-Pro:python-lib caiomsouza$ cd python-louvain-0.3
Caios-MacBook-Pro:python-louvain-0.3 caiomsouza$ ls
PKG-INFO community setup.cfg
README python_louvain.egg-info setup.py
Caios-MacBook-Pro:python-louvain-0.3 caiomsouza$ sudo python setup.py install
Output:
Caios-MacBook-Pro:python-louvain-0.3 caiomsouza$ sudo python setup.py install
running install
/Users/caiomsouza/anaconda/lib/python2.7/site-packages/setuptools-14.3-py2.7.egg/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2512: PEP440Warning: 'llvmlite (0.2.2-1-gbcb15be)' is being parsed as a legacy, non PEP 440, version. You may find odd behavior and sort order. In particular it will be sorted as less than 0.0. It is recommend to migrate to PEP 440 compatible versions.
running bdist_egg
running egg_info
writing requirements to python_louvain.egg-info/requires.txt
writing python_louvain.egg-info/PKG-INFO
writing top-level names to python_louvain.egg-info/top_level.txt
writing dependency_links to python_louvain.egg-info/dependency_links.txt
writing entry points to python_louvain.egg-info/entry_points.txt
reading manifest file 'python_louvain.egg-info/SOURCES.txt'
writing manifest file 'python_louvain.egg-info/SOURCES.txt'
installing library code to build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg
running install_lib
running build_py
creating build
creating build/lib
creating build/lib/community
copying community/__init__.py -> build/lib/community
creating build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64
creating build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg
creating build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/community
copying build/lib/community/__init__.py -> build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/community
byte-compiling build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/community/__init__.py to __init__.pyc
creating build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/EGG-INFO
copying python_louvain.egg-info/PKG-INFO -> build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/EGG-INFO
copying python_louvain.egg-info/SOURCES.txt -> build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/EGG-INFO
copying python_louvain.egg-info/dependency_links.txt -> build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/EGG-INFO
copying python_louvain.egg-info/entry_points.txt -> build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/EGG-INFO
copying python_louvain.egg-info/requires.txt -> build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/EGG-INFO
copying python_louvain.egg-info/top_level.txt -> build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/EGG-INFO
zip_safe flag not set; analyzing archive contents...
creating dist
creating 'dist/python_louvain-0.3-py2.7.egg' and adding 'build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg' to it
removing 'build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg' (and everything under it)
Processing python_louvain-0.3-py2.7.egg
Copying python_louvain-0.3-py2.7.egg to /Users/caiomsouza/anaconda/lib/python2.7/site-packages
Adding python-louvain 0.3 to easy-install.pth file
Installing community script to /Users/caiomsouza/anaconda/bin
Installed /Users/caiomsouza/anaconda/lib/python2.7/site-packages/python_louvain-0.3-py2.7.egg
Processing dependencies for python-louvain==0.3
Searching for networkx==1.9.1
Best match: networkx 1.9.1
Adding networkx 1.9.1 to easy-install.pth file
Using /Users/caiomsouza/anaconda/lib/python2.7/site-packages
Finished processing dependencies for python-louvain==0.3
Note for Linux Ubuntu Users:
If you are using Linux Ubuntu you will maybe need to install setuptools.
export PATH=/opt/anaconda/bin/:$PATH;
ipython notebook
Louvain algorithm for community detection
1) download from: https://pypi.python.org/pypi/python-louvain/0.3
2) Unzip python-louvain-0.3.tar.gz
3) Run on terminal the command sudo python setup.py install in side the unzip folder called python-louvain-0.3
4) Restart ipython notebook
5) Try it.
Last login: Sat Jun 13 10:25:49 on ttys000
Caios-MacBook-Pro:u-tad caiomsouza$ sudo python setup.py install
Password:
python: can't open file 'setup.py': [Errno 2] No such file or directory
Caios-MacBook-Pro:u-tad caiomsouza$ ls
Mod1 Mod15 Mod5 contributors.txt
Mod10 Mod16 Mod6 material-internet
Mod11 Mod17 Mod7 planning_EDS_2ED.pdf
Mod12 Mod2 Mod8
Mod13 Mod3 Mod9
Mod14 Mod4 actividades-utad.xlsx
Caios-MacBook-Pro:u-tad caiomsouza$ cd Mod9/
Caios-MacBook-Pro:Mod9 caiomsouza$ ls
GD_M09_Grafos_SNA.pdf datasets python-lib slides
Caios-MacBook-Pro:Mod9 caiomsouza$ cd python-lib/
Caios-MacBook-Pro:python-lib caiomsouza$ ls
python-louvain-0.3.tar.gz
Caios-MacBook-Pro:python-lib caiomsouza$ ls
python-louvain-0.3 python-louvain-0.3.tar.gz
Caios-MacBook-Pro:python-lib caiomsouza$ cd python-louvain-0.3
Caios-MacBook-Pro:python-louvain-0.3 caiomsouza$ ls
PKG-INFO community setup.cfg
README python_louvain.egg-info setup.py
Caios-MacBook-Pro:python-louvain-0.3 caiomsouza$ sudo python setup.py install
Output:
Caios-MacBook-Pro:python-louvain-0.3 caiomsouza$ sudo python setup.py install
running install
/Users/caiomsouza/anaconda/lib/python2.7/site-packages/setuptools-14.3-py2.7.egg/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2512: PEP440Warning: 'llvmlite (0.2.2-1-gbcb15be)' is being parsed as a legacy, non PEP 440, version. You may find odd behavior and sort order. In particular it will be sorted as less than 0.0. It is recommend to migrate to PEP 440 compatible versions.
running bdist_egg
running egg_info
writing requirements to python_louvain.egg-info/requires.txt
writing python_louvain.egg-info/PKG-INFO
writing top-level names to python_louvain.egg-info/top_level.txt
writing dependency_links to python_louvain.egg-info/dependency_links.txt
writing entry points to python_louvain.egg-info/entry_points.txt
reading manifest file 'python_louvain.egg-info/SOURCES.txt'
writing manifest file 'python_louvain.egg-info/SOURCES.txt'
installing library code to build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg
running install_lib
running build_py
creating build
creating build/lib
creating build/lib/community
copying community/__init__.py -> build/lib/community
creating build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64
creating build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg
creating build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/community
copying build/lib/community/__init__.py -> build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/community
byte-compiling build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/community/__init__.py to __init__.pyc
creating build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/EGG-INFO
copying python_louvain.egg-info/PKG-INFO -> build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/EGG-INFO
copying python_louvain.egg-info/SOURCES.txt -> build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/EGG-INFO
copying python_louvain.egg-info/dependency_links.txt -> build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/EGG-INFO
copying python_louvain.egg-info/entry_points.txt -> build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/EGG-INFO
copying python_louvain.egg-info/requires.txt -> build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/EGG-INFO
copying python_louvain.egg-info/top_level.txt -> build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg/EGG-INFO
zip_safe flag not set; analyzing archive contents...
creating dist
creating 'dist/python_louvain-0.3-py2.7.egg' and adding 'build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg' to it
removing 'build/bdist.macosx-10.5-x86_64/egg' (and everything under it)
Processing python_louvain-0.3-py2.7.egg
Copying python_louvain-0.3-py2.7.egg to /Users/caiomsouza/anaconda/lib/python2.7/site-packages
Adding python-louvain 0.3 to easy-install.pth file
Installing community script to /Users/caiomsouza/anaconda/bin
Installed /Users/caiomsouza/anaconda/lib/python2.7/site-packages/python_louvain-0.3-py2.7.egg
Processing dependencies for python-louvain==0.3
Searching for networkx==1.9.1
Best match: networkx 1.9.1
Adding networkx 1.9.1 to easy-install.pth file
Using /Users/caiomsouza/anaconda/lib/python2.7/site-packages
Finished processing dependencies for python-louvain==0.3
Note for Linux Ubuntu Users:
If you are using Linux Ubuntu you will maybe need to install setuptools.
export PATH=/opt/anaconda/bin/:$PATH;
ipython notebook
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)